ICG Technology
The ICG is a non-invasive cardiac output monitoring solution, created for healthcare professionals and hospitals. Our cardiac output solution utilizes the thoracic impedance signal to calculate key parameters related to cardiac output.
This technology is used to guide the healthcare professionals in determining the cardiac output of a patient through thoracic blood flow monitoring.
ICG Technology Works
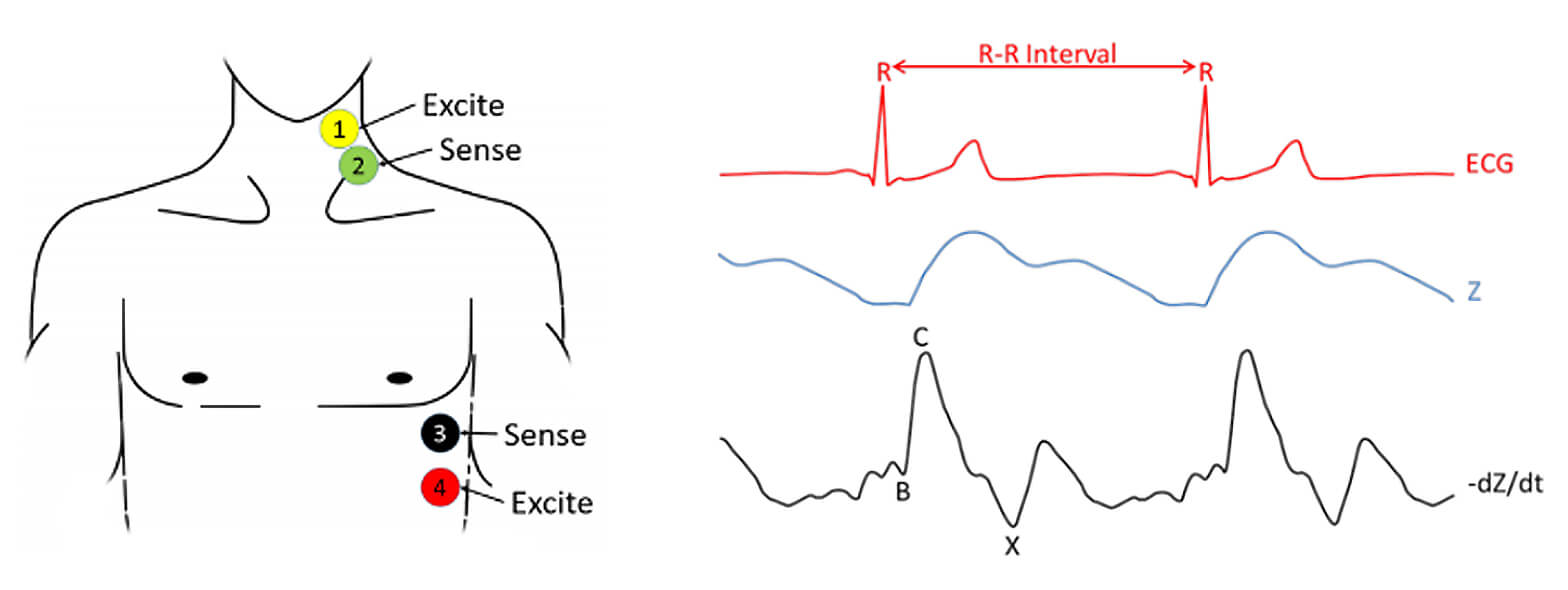
The impedance cardiography (ICG) and electrocardiogram (ECG) by using 4 electrodes, with one pair injecting a constant current, and a second pair of electrodes measuring the resulting voltage.
The ICG signal represents the changes of the thoracic impedance due to variations in the blood flow. In practice, the raw Z signal is transformed into the –dZ/dt waveform by using the first derivative to remark the inflection points of the raw Z signal. This signal is post-processed to increase its quality.
The most important characteristic points of the ICG impedance signal are their maxima (C) and their preceding minima (B). These points are associated to distinct physiological events within the systolic part of the cardiac cycle: B points are the downward deflection due to the contraction of the atria and C points are the major upward deflection occurring during systole. In that sense, the R wave from the ECG signal is an important reference for detecting such events. The ICG algorithm locates these points, which relate to the stroke volume of the patient. The main problems arising from these point locations involve noise detection and movement of the patient, since the signals are highly sensitive. Different algorithms to prevent noise and artifacts are implemented in the ICG device.
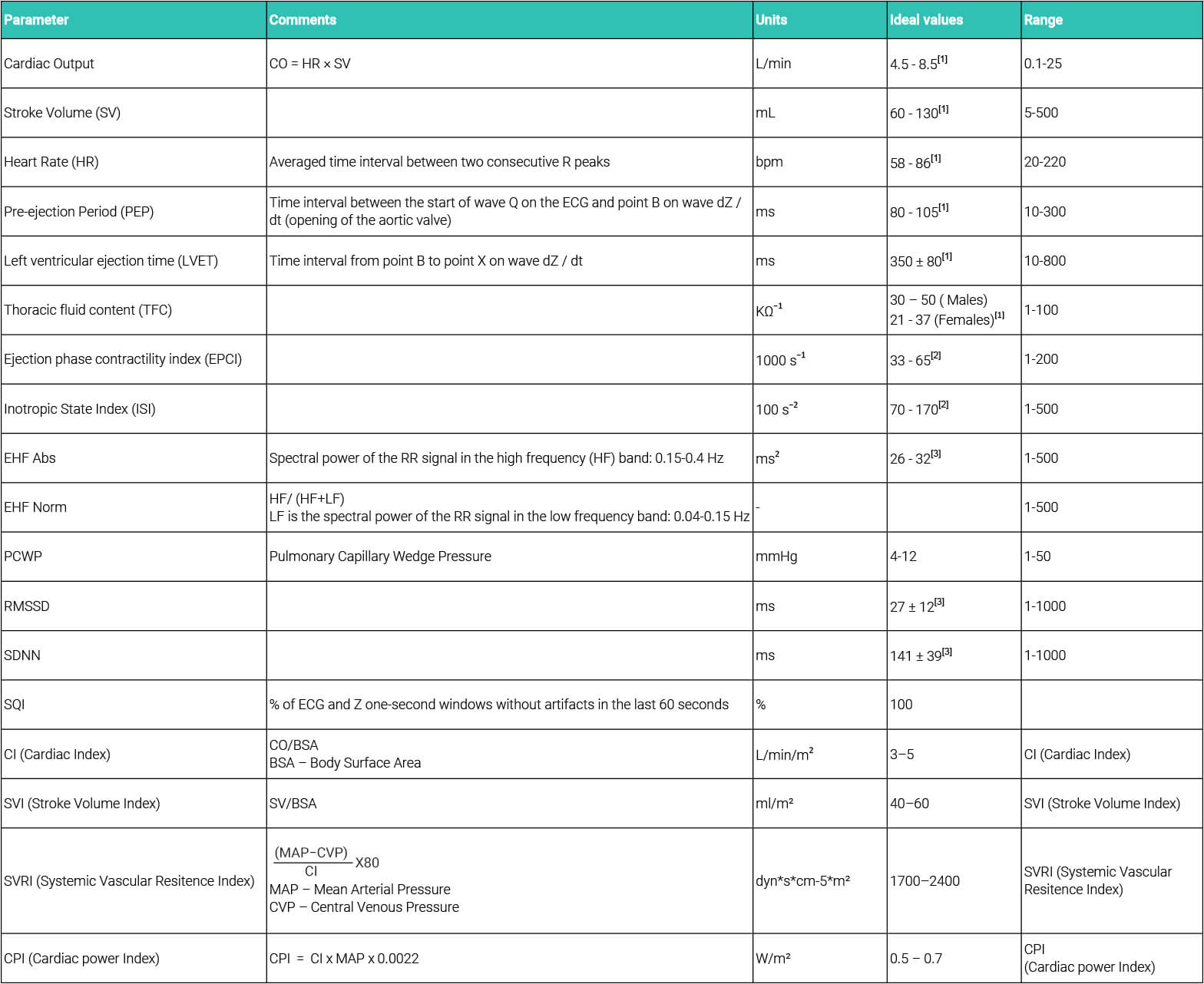
ICG Calculation Parameters
ICG Clinical Validation
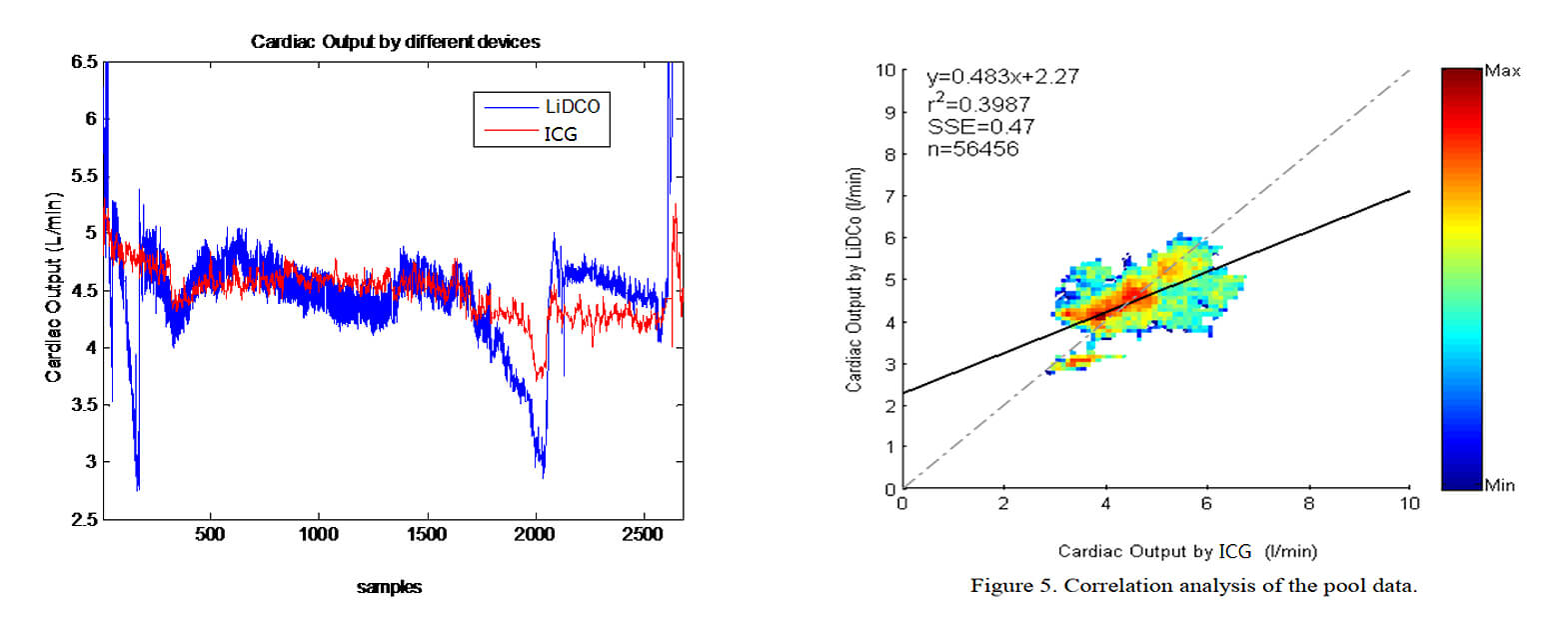
Data from 13 patients, 8 males and 5 females were included into final analysis. Not a single patient suffered
from any complication in the context of the present study. Blood loss, fluid administration and hypotension
periods after induction were not included into our analysis. it is visible that ICG ,LiDCO rapid and NICOM share a common overall trend. However, LiDCO rapid shows several sudden drops in cardiac output for which there is no reported clinical evidence and which are not followed by the ICG monitor.
In conclusion, the results suggest that cardiac output calculated with the ICG monitor is comparable to the
values calculated by the LiDCO rapid and NICOM monitor. the ICG has demonstrated a very low bias with the LiDCOrapid monitor and NICOM in a variety of different situations.
ICG Clinical Benefits
● Help diagnose,triage, or choose and anticipate the response to treatment in different cases such as cardiopathies, heart failure, hypertension, trauma, sepsis, burn, hypovolemic shock or dyspnea.
●Detection and potencial correction in situations of hypovolemia and hypervolemia.
● Monitoring high-risk patients undergoing any surgery (as long as it does not affect the thorax morphology).
● Ideal for use in Intensive Care Units (ICU).
●Detection and potencial correction in situations of hypovolemia and hypervolemia.
● Monitoring high-risk patients undergoing any surgery (as long as it does not affect the thorax morphology).
● Ideal for use in Intensive Care Units (ICU).
● Guide the Goal-directed therapy (GDT), for the administration of fluids or inotropes in order to optimize preload, contractility and afterload.
● Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) can benefit of the use of CCO by fluid management optimization.
● Improve cost-efficiency of the hospital, mainly by improving the outcome through shorter hospital stay, thus saving highly expensive resources.
● Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) can benefit of the use of CCO by fluid management optimization.
● Improve cost-efficiency of the hospital, mainly by improving the outcome through shorter hospital stay, thus saving highly expensive resources.
Monitoring of Cardiac Output provides valuable information that should be used to establish a treatment plan and apply targeted therapy as soon as possible.
The key advantage of the CCO lies in the validated and improved technology with respect to leading products on the market.
Related Products